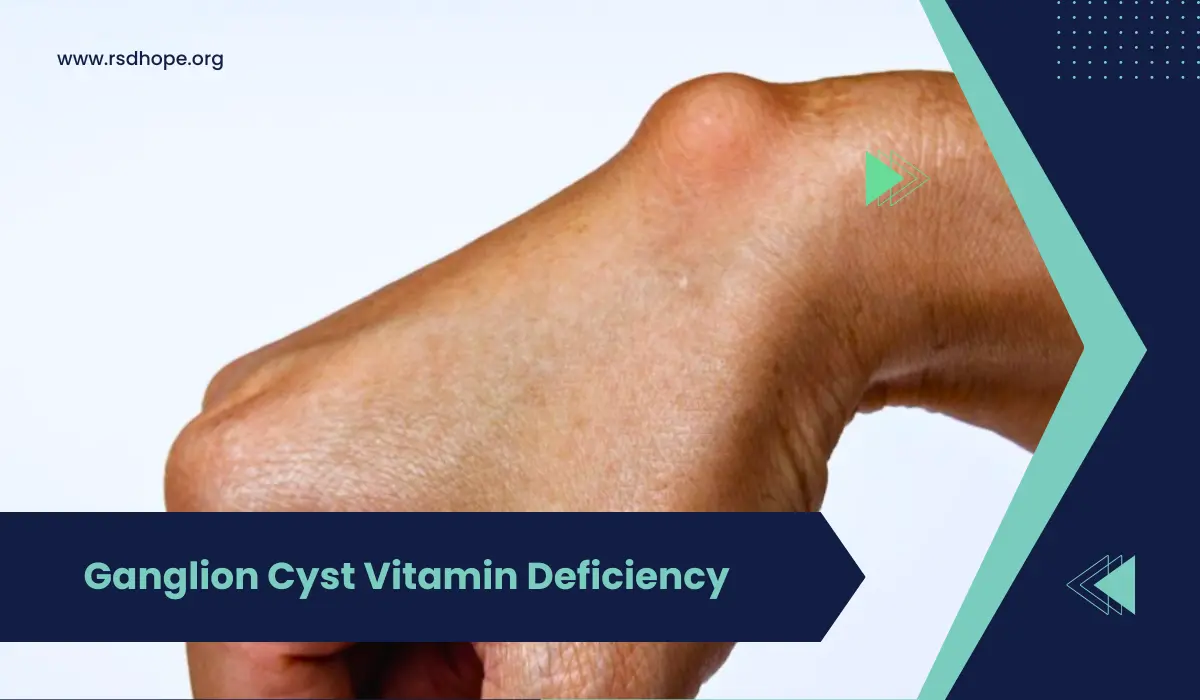
Have you ever noticed a small, round lump on your wrist or hand? Chances are, it might be a ganglion cyst. These noncancerous growths can cause discomfort or pain, but did you know that vitamin deficiency may play a role in their development? In this blog post, we’ll explore the fascinating connection between ganglion cysts and vitamin deficiency, shedding light on how your diet may impact your risk of developing these lumps.
Key Takeaways
- Ganglion cysts are noncancerous lumps that commonly occur on the wrists or hands.
- Vitamin deficiency, particularly vitamin B6 deficiency, may contribute to the development of ganglion cysts.
- Maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins can help support overall health and potentially reduce the risk of ganglion cysts.
Understanding Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts are soft, fluid-filled lumps that typically develop along the tendons or joints of the wrists or hands. These round or oval-shaped growths can vary in size, ranging from a pea to a golf ball. While ganglion cysts are usually painless, they can cause discomfort or pain when pressing on a nerve or restricting joint movement.
The exact cause of ganglion cysts remains unknown, but they are believed to form when the synovial fluid that lubricates the joints or tendons leaks out and accumulates in a sac. This leakage may occur due to joint or tendon irritation, mechanical changes, or trauma.
The Role of Vitamins in the Body
Vitamins are essential nutrients that play a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. These organic compounds are required in small amounts to support various bodily functions, including:
- Boosting immune function
- Maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails
- Supporting bone health
- Aiding in energy production
- Promoting healthy brain function
A deficiency in certain vitamins can lead to various health issues, ranging from mild symptoms to severe conditions. For example, vitamin D deficiency can cause weak bones, while vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to anemia and neurological problems.
Common Vitamins Linked to Ganglion Cyst Formation
While the exact cause of ganglion cysts remains unknown, some studies suggest that vitamin deficiency may play a role in their development. The most commonly associated vitamins include:
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
These vitamins are crucial for maintaining healthy nerves, connective tissues, and bones, all of which are involved in the proper functioning of the joints and tendons where ganglion cysts typically form.
Vitamin B6 Deficiency and Ganglion Cysts
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including protein metabolism, red blood cell formation, and nervous system health. This vitamin is also essential for the synthesis of collagen, a protein that provides structure and strength to the connective tissues in the body.
A deficiency in vitamin B6 can lead to abnormalities in collagen production, potentially contributing to the development of ganglion cysts.
When collagen production is impaired, the connective tissues around the joints and tendons may become weakened, making them more susceptible to injury or irritation.
Other Vitamins and Ganglion Cysts
In addition to vitamin B6, other vitamins may also play a role in the development of ganglion cysts:
- Vitamin C: This antioxidant vitamin is essential for collagen synthesis and maintaining healthy connective tissues. A deficiency in vitamin C can lead to weakened tendons and ligaments, potentially increasing the risk of ganglion cysts.
- Vitamin D: Known for its role in bone health, vitamin D also helps regulate calcium absorption and supports healthy immune function. Some studies suggest that vitamin D deficiency may contribute to the development of ganglion cysts, although more research is needed to confirm this link.
Diagnosing Ganglion Cysts
If you suspect you have a ganglion cyst, your healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination to assess the lump’s size, location, and mobility. They may also recommend imaging tests, such as X-rays or ultrasounds, to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions that may mimic ganglion cysts, such as tumors or arthritis.
Diagnosing vitamin deficiency as a direct cause of ganglion cysts can be challenging, as the relationship between the two is not yet fully understood. However, your healthcare provider may recommend blood tests to assess your vitamin levels and determine if a deficiency is present.
Treating Ganglion Cysts
Treatment for ganglion cysts depends on their size, location, and the severity of symptoms. In many cases, ganglion cysts resolve on their own without any intervention. However, if the cyst is causing pain or interfering with daily activities, treatment options may include:
- Observation: If the cyst is small and not causing any discomfort, your healthcare provider may recommend a “wait and see” approach.
- Aspiration: In this procedure, a fine needle is used to drain the fluid from the cyst, reducing its size and relieving pressure on the surrounding tissues.
- Surgery: If the cyst is large, painful, or recurrent, your healthcare provider may recommend surgical removal.
In addition to these treatment options, addressing any underlying vitamin deficiencies through a balanced diet or supplementation may help support overall joint health and potentially reduce the risk of ganglion cysts.
Preventing Ganglion Cysts
While there is no surefire way to prevent ganglion cysts, maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins may help support joint health and reduce the risk of developing these lumps. Some tips for preventing ganglion cysts include:
- Eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Include vitamin B6-rich foods in your diet, such as poultry, fish, potatoes, and non-citrus fruits.
- Getting enough vitamin C from citrus fruits, berries, tomatoes, and leafy greens.
- Ensuring adequate vitamin D intake through safe sun exposure, fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products.
- Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the joints and tendons.
- Practicing good posture and ergonomics to minimize strain on the wrists and hands.
If you have a family history of ganglion cysts or are concerned about your risk, talk to your healthcare provider about additional prevention strategies and monitoring.
Also Read: Signs Of Vitamin Deficiency In Nails
Conclusion
While the exact cause of ganglion cysts remains unknown, emerging evidence suggests that vitamin deficiency may play a role in their development. By understanding the importance of essential vitamins like B6, C, and D for joint health, you can take proactive steps to support your body and potentially reduce your risk of developing these noncancerous lumps.
If you suspect you have a ganglion cyst or are experiencing joint discomfort, don’t hesitate to consult your healthcare provider. They can help diagnose the issue, recommend appropriate treatment options, and guide you in maintaining a balanced diet to support your overall health and well-being.
Remember, your body thrives on a foundation of proper nutrition, so nourish it with the essential vitamins and nutrients it needs to keep you feeling your best.
FAQs
A: While vitamin supplements may help address any underlying deficiencies, they are not a standalone treatment for ganglion cysts. If you suspect you have a vitamin deficiency, consult your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action. They may recommend dietary changes, supplements, or other interventions based on your individual needs.
A: Ganglion cysts are typically benign and do not indicate a serious underlying health issue. However, in rare cases, a lump that appears to be a ganglion cyst may be a sign of a more serious condition, such as a tumor or infection. If you have any concerns about a lump on your wrist or hand, it’s best to consult your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.
A: While a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins may help support joint health, it is not a guaranteed way to prevent ganglion cysts. Other factors, such as genetics, joint stress, and trauma, may also contribute to the development of these lumps. However, maintaining a healthy diet can support overall well-being and may help reduce the risk of ganglion cysts in some individuals.
A: Vitamin B6 is found in a variety of foods, including poultry, fish, potatoes, and non-citrus fruits. According to the National Institutes of Health, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for vitamin B6 is 1.3 milligrams for adults aged 19-50 years, and slightly higher for older adults. If you are concerned about your vitamin B6 intake, talk to your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian about incorporating more B6-rich foods into your meals or considering a supplement if necessary. Remember, it’s always best to obtain nutrients from whole food sources whenever possible.